Understanding Differences Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Overview of Glands
The human body’s glands are specialised structures. They are essential for preserving physiological balance and ensuring the effective operation of various body processes. These organs are responsible for producing chemicals like hormones, enzymes, and other significant compounds involved in metabolic processes. The body uses two primary types of glands: endocrine and exocrine glands. These glands serve different but equally vital purposes.
Endocrine Glands
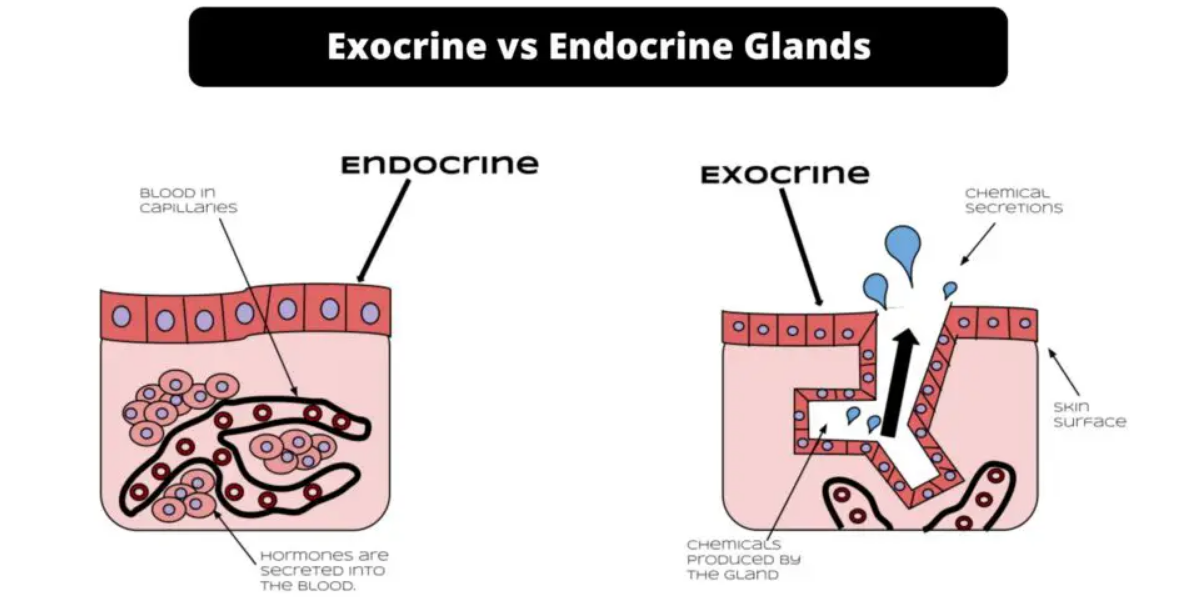
Endocrine glands directly release their products into the bloodstream. This secretion mechanism allows hormones to travel throughout the body. As a result, hormones impact many bodily functions, such as development, metabolism, and mood control. The pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands are important types of endocrine glands. These glands provide both short-term and long-term responses to internal and external stimuli. This makes them essential for the body’s hormonal control.
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands, on the other hand, release their products via ducts to specific locations. These products often go onto the surfaces of epithelial cells. Saliva, perspiration, and digestive enzymes are among the many products produced by these glands. Salivary glands, sweat glands, and the pancreas, which performs both exocrine and endocrine functions, are examples of exocrine glands. Exocrine glands play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. The compounds they secrete are essential for functions like digestion and thermoregulation.
Working Together: Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
For the body to operate effectively, the endocrine and exocrine glands must work together. Exocrine glands are essential for localised activities, while endocrine glands mainly affect bodily functions through hormonal signalling. Understanding the differences between these two types of glands helps to see how each contributes to different physiological systems. This leads to a more thorough examination of their unique traits and roles.
Features of the Endocrine Glands
What Are Endocrine Glands?
Endocrine glands are specialised structures. They are essential for controlling various physiological functions in the body. Unlike exocrine glands, which release chemicals through ducts to specific locations, endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream. This method allows hormones to travel throughout the body and affect distant target organs and tissues. Endocrine glands are crucial for maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Examples of Major Endocrine Glands
The pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and pancreatic glands are some of the main endocrine glands. The pituitary is known as the “master gland.” It generates several vital hormones, such as prolactin, growth hormone, and other hormones that control the activity of other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels. The adrenal glands produce hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are vital for the body’s stress response and play important roles in metabolism and immune functions. Additionally, the pancreas is an exocrine and endocrine gland. It generates glucagon and insulin, both of which control blood sugar levels.
The Importance of Endocrine Glands
The importance of endocrine glands lies in the way their hormones interact with different bodily systems. For example, the hypothalamus works with the pituitary gland to adjust hormone levels in response to the body’s needs. Endocrine glands impact a person’s health by regulating metabolism, growth, development, and reproduction. The endocrine system helps maintain equilibrium in the body through a complex web of feedback mechanisms. This underscores the importance of these glands in both health and disease.
Features of the Exocrine Glands
What Are Exocrine Glands?
Exocrine glands are specialised glands. They are responsible for secreting chemicals directly onto the surface of epithelial cells, usually through ducts. Unlike endocrine glands, which release hormones into the bloodstream, exocrine glands transport fluid substances such as enzymes, perspiration, and saliva to specific locations. Many physiological processes that support digestion, thermoregulation, and homeostasis depend on the secretion from exocrine glands.
The Ductal Structure of Exocrine Glands
One of the main features of exocrine glands is their ductal structure. This structure helps transport secretions to specific parts of the body. For example, the salivary glands produce saliva to help digest food. The saliva’s ducts lead directly to the mouth cavity, where it is released to start the digestive process. Similarly, sweat glands produce perspiration, which travels through ducts to the surface of the skin. This helps regulate body temperature during physical activity or when exposed to high temperatures.
Pancreas: A Dual Function Gland
The pancreas is another interesting example of an exocrine gland. It has both exocrine and endocrine functions. It releases glucagon and insulin into the bloodstream as part of its endocrine function. The exocrine part of the pancreas produces digestive enzymes like lipase and amylase. These enzymes are transported to the small intestine via pancreatic ducts to break down fats and carbohydrates. While exocrine and endocrine glands share some similarities, their primary functions and modes of activity are quite different.
Summary of Exocrine Gland Functions
In summary, the primary characteristics of exocrine glands centre around their ability to produce chemicals that are transported to specific target locations via ducts. This feature, which distinguishes exocrine glands from the hormone-releasing endocrine glands, is vital for processes such as digestion, temperature regulation, and other physiological functions.
Important Distinctions and Health Consequences
Understanding the Significance of Endocrine Glands
To understand human physiology and health, it is crucial to distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. Endocrine glands, including the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, release hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones circulate throughout the body, affecting various target organs and tissues. The chemicals produced by endocrine glands are essential for regulating growth, development, metabolism, and overall balance. Disorders in these glands, such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism, or adrenal insufficiency, can significantly impact health.
Exocrine Glands and Their Health Impact
Exocrine glands, such as the salivary, sweat, and digestive glands, release their secretions through ducts to external environments or cavities. These secretions, which may include bile, sweat, saliva, or enzymes, play vital roles in digestion, waste elimination, and temperature regulation. Exocrine gland failure can lead to health problems such as pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis, highlighting the importance of these glands in maintaining proper body functions.
Health Consequences of Dysfunction in Glands
Developmental or functional problems in any type of gland can lead to various health issues. Hormone imbalances caused by the dysfunction of endocrine glands may result in a range of health problems requiring medical attention. Similarly, secretory disorders resulting from blockages or malfunctions in exocrine glands can cause significant health challenges. Both patients and healthcare professionals need to understand these distinctions to accurately diagnose and address their consequences for overall health. Homeostasis and proper body function rely on the efficient action of both endocrine and exocrine glands.



