Understanding Prostatitis and Prostate Cancer
There are two different conditions that affect men’s prostate glands: prostatitis and prostate cancer. Prostatitis is a medical term that refers to inflammation of the prostate gland caused by a variety of conditions or bacterial infections. Prostate soreness or discomfort, frequent urination, and trouble urinating are all possible signs of prostatitis. Antibiotics or other drugs, depending on the underlying reason, are often used to treat it.
Exploring Prostate Cancer
A tumour that grows malignantly in the prostate gland is called prostate cancer. Prostate cancer, unlike prostatitis, is caused by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells within the prostate rather than inflammation. Urine with blood in it, erectile dysfunction, and bone pain are all possible signs of prostate cancer. Surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy are possible treatments for prostate cancer, contingent on the cancer’s stage and severity.
Differentiating Prostatitis and Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis and prostate cancer both affect the prostate gland, but they are distinct illnesses with different causes and treatment options. Unlike prostate cancer, which is a dangerous illness characterised by the growth of cancerous cells, prostatitis is frequently an inflammatory, non-cancerous condition. It’s critical that men understand the signs of both disorders and get medical help if they have any worrying symptoms pertaining to their prostate health. Routine examinations and screenings may help with the early detection and treatment of prostate-related issues.
An Introduction to Prostate Cancer and Prostatitis
In the male reproductive system, the prostate gland is essential. This tiny, walnut-sized gland, located in front of the rectum and just below the bladder, secretes the seminal fluid that feeds and moves sperm during ejaculation. Any illness affecting the prostate may have a major impact on a man’s health and well-being because of its crucial role.
Understanding Prostatitis
Prostate cancer and prostatitis are two prevalent disorders that may affect the prostate. Prostatitis, or inflammation of the prostate gland, can cause a variety of symptoms, including discomfort, difficulty urinating, and sexual dysfunction. It is a quite prevalent ailment, especially in males under 50. Depending on the length and intensity of the symptoms, prostatitis may be either bacterial or non-bacterial and manifest as either acute or chronic.
Exploring Prostate Cancer in Detail
Prostate cancer, however, is a malignant development that originates from the prostate gland’s cells. It is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer among men, especially those over 65. In its early stages, prostate cancer often progresses slowly and may not show any symptoms at all. Yet, if the cancer worsens, it may cause more serious health problems, such as spreading to other bodily regions.
Understanding the Reasons and Hazards
It’s essential to distinguish between prostatitis and prostate cancer by knowing their respective causes and risk factors. Numerous reasons may cause prostatitis, which is an inflammation of the prostate gland. Bacterial infections are often the result of germs migrating to the prostate from the urinary system. Non-bacterial prostatitis is more intricate and may arise from several factors, such as immune system reactions, pelvic trauma, or stress. It is distinct from bacterial prostatitis.
Identifying Risk Factors
In non-bacterial prostatitis, stress is a major factor. Stress on both a physical and emotional level may cause inflammation and muscle tension in the pelvic region, which exacerbates symptoms. Moreover, autoimmune reactions—in which the immune system of the body unintentionally targets the prostate tissue—are also linked to chronic prostatitis. These varied origins highlight how complex prostatitis is.
Exploring Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
On the other hand, the causes of prostate cancer are more strongly associated with environmental and hereditary variables. Men with a family history of prostate cancer are more susceptible due to a genetic predisposition, which is a major risk factor. Age is another important consideration, as the risk increases dramatically after the age of 50. Racial inequities are also apparent, given that USA and African males are more likely to have health problems than men of other races.
 Understanding Lifestyle Factors
Understanding Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and exposure to environmental pollutants all contribute to the risk of developing prostate cancer. Diets high in dairy and red meat, with little to no fruit or vegetable consumption, are associated with increased risks. Obesity and insufficient exercise both increase the risk. The risk of getting prostate cancer has been linked to exposure to several environmental factors, including radiation and certain chemicals.
Exploring Signs and Diagnosis
Effective management and treatment of prostatitis and prostate cancer require a thorough understanding of the symptoms and diagnostic processes associated with prostatitis disorders. While they both affect the prostate gland, there are notable differences in their symptoms and methods of diagnosis.
Understanding Prostatitis Symptoms
A variety of symptoms are often present in prostatitis, an infection of the prostate gland. Urinary issues, such as difficulties starting a pee session or frequent urination, pelvic pain, and discomfort after ejaculation, are common symptoms. In addition, patients may feel cold and feverish, similar to the flu, especially if they have acute bacterial prostatitis. On the other hand, the symptoms of chronic prostatitis are usually more subtle, including ongoing pelvic discomfort and urine problems over time.
Exploring Prostate Cancer Symptoms
However, prostate cancer may not present with any symptoms when it is first discovered, which is why routine screening is crucial. When they do occur, symptoms may include pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, weak or intermittent urine flow, and blood in the urine or semen. The symptoms of advanced prostate cancer, which point to the cancer’s metastasis beyond the prostate gland, include weariness, weight loss, and bone discomfort.
Diagnostic Techniques
A digital rectal exam (DRE) and other physical examinations are often used in conjunction with laboratory testing, urine analysis, and cultures to detect bacterial infections and diagnose prostatitis. To evaluate the disease, imaging procedures like MRIs and ultrasounds may also be performed. To find inflammation, a prostate fluid study may be performed in specific circumstances.
Diagnostic Procedures for Prostate Cancer
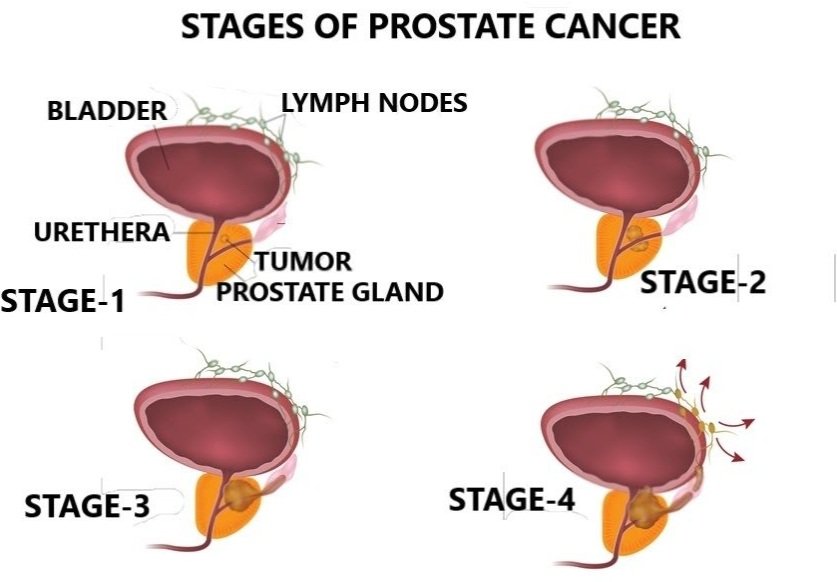
A DRE and a PSA blood test are often the first steps in the diagnosis procedure for prostate cancer. While more testing is required for a clear diagnosis, elevated PSA levels may be indicative of prostate cancer. Bone scans and MRIs are two imaging techniques that are used to assess the cancer’s extent. The gold standard for determining the existence of malignant cells in the prostate is still a biopsy, which involves taking a tiny sample of tissue and looking at it under a microscope.
Understanding Therapy and Outlook
Due to their different underlying causes and characteristics, prostatitis and prostate cancer have very different treatment choices. Non-infectious causes of prostate gland inflammation, also known as prostatitis, include bacterial infections. Antibiotics, which are usually taken for a few weeks, are the main therapies for bacterial prostatitis. Extended antibiotic regimens may be required in patients with persistent bacterial prostatitis.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Alpha-blockers and anti-inflammatory drugs, on the other hand, are often used to treat non-bacterial prostatitis in order to relax the muscles in the bladder, neck, and prostate. Modest dietary changes, frequent exercise, and an increase in hydration consumption are examples of lifestyle modifications that may be quite helpful in reducing symptoms.
Therapeutic Approaches for Prostate Cancer
The treatment options for prostate cancer are more complicated and change according to the cancer’s stage and degree of aggression. Active surveillance, which includes routine monitoring with PSA testing and biopsies, may be used to treat early-stage prostate cancer. Surgical procedures, such as radical prostatectomy, which entails removing the prostate gland, are examples of more intrusive therapies. High-energy rays are used in radiation therapy, another popular treatment, to target and kill cancer cells. In more advanced instances, chemotherapy is used to destroy cancer cells that are dividing quickly, while hormone treatment tries to lower levels of male hormones that might encourage the development of cancer.
Examining Prognosis
Both prostatitis and prostate cancer have differing prognoses. The prognosis for prostatitis is usually favourable when treated quickly with the right drugs; however, chronic cases may need continued care. On the other hand, the prognosis for prostate cancer is largely based on the cancer’s stage at diagnosis and early discovery. Many people with localised prostate cancer go on to have long lives after receiving therapy, indicating a high percentage of survival. On the other hand, managing metastatic prostate cancer that has progressed beyond the prostate gland offers additional difficulties and can call for a mix of therapies.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
For both illnesses, early diagnosis is crucial. Regular check-ups may help detect problems early, increasing the likelihood of effective treatment and improved results. Examples of these check-ups include PSA testing and digital rectal examinations. It is essential for patients and healthcare professionals to understand the distinctions between prostatitis and prostate cancer in order to ensure that each ailment is managed with a customised strategy and with the best possible prognosis.
Table of Differences between Prostatitis and Prostate Cancer
| Characteristic | Prostatitis | Prostate Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation or infection of the prostate gland | Malignant growth of cells in the prostate gland |
| Cause | Bacterial infection, pelvic trauma, or unknown causes | exact cause is unknown; genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors may play a role |
| Symptoms | Painful urination, pelvic pain, urinary frequency | There are no symptoms in early stages; later stages may include difficulty urinating, blood in urine, and erectile dysfunction |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, urine tests, prostate massage, and imaging tests | PSA blood test, digital rectal exam, biopsy, and imaging tests |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, alpha-blockers, and pain relievers | Active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy |
| Progression | It generally resolves with treatment but may become chronic | Can spread beyond the prostate to other organs and tissues |
| Prevalence | Common, affecting men of all ages | The second-most common cancer in men worldwide |
| Risk Factors | Age, history of urinary tract infections, sexual activity | Age, family history, race (more common in African American men), diet, and lifestyle |
| Prognosis | Good with appropriate treatment; may recur | Varies depending on stage and treatment; early detection improves prognosis |
| Screening | Not routinely screened for; diagnosed based on symptoms and tests | PSA blood test and digital rectal exams may be used for screening, but they are controversial due to risk of overdiagnosis and overtreatment |



